As a fully insured and licensed company, Conquer Termites complies with all the requirements and guidance given by our insurer – Rapid Solutions, the Australian Standards and the manufacturer’s instructions.
But there are real limitations to the work we conduct. It is important that you, our customer clearly understand these, so we can work together for the right outcome:
Terms & limitations:
1. THIS IS A VISUAL INSPECTION ONLY in accord with the requirements of AS 4349.3 Inspection of buildings Part 3: Timber pest inspections. Visual inspection was limited to those areas and sections of the property to which reasonable access (See Definition) was both available and permitted on the date of Inspection. The inspection DID NOT include breaking apart, dismantling, removing or moving objects including, but not limited to, foliage, mouldings, roof insulation/sisalation, floor or wall coverings, sidings, ceilings, floors, furnishings, appliances or personal possessions. The inspector CANNOT see inside walls, between floors, inside skillion roofing, inside the eaves, behind stored goods in cupboards, and in other areas that are concealed or obstructed.
The inspector DID NOT dig, gouge, force or perform any other invasive procedures. An invasive inspection will not be performed unless a separate contract is entered into. In an occupied property it must be understood that furnishings or household items may be concealing evidence of Timber Pests which may only be revealed when the items are moved or removed. In the case of Strata type properties only the interior of the unit is inspected.
2. SCOPE OF REPORT: This Report is confined to reporting on the discovery, or non-discovery, of infestation and/or damage caused by subterranean and damp wood termites (white ants), borers of seasoned timber and wood decay fungi (hereinafter referred to as “Timber Pests”), present on the date of the Inspection. The Inspection did not cover any other pests and this Report does not comment on them. Dry wood termites (Family: KALOTERMITIDAE) and European House Borer (Hylotrupes bujulus Linnaeus) were excluded from the Inspection, but have been reported on if, in the course of the Inspection, any visual evidence of infestation happened to be found. If Cryptotermes brevis (West Indian Dry Wood Termite) or Hylotrupes bujulus Linnaeus are discovered we are required by law to notify Government Authorities. If reported a special purpose report may be necessary.
3. LIMITATIONS: Nothing contained in the Report implies that any inaccessible or partly inaccessible areas or sections of the property being inspected by the Inspector on the date of the inspection were not, or have not been, infested by Timber Pests. Accordingly, this Report is not a guarantee that an infestation and/or damage does not exist in any inaccessible or partly inaccessible areas or sections of the property. Nor is it a guarantee that a future infestation of Timber Pests will not occur or be found.
4. DETERMINING EXTENT OF DAMAGE: TThe Report is NOT a structural damage Report. We claim no expertise in building and any inexpert opinion we give on timber damage CANNOT be relied upon. The Report will not state the full extent of any timber pest damage. The Report will state timber damage found as ‘slight’, `moderate’, `moderate to extensive’ or ‘extensive’. This information is not the opinion of an expert. If any evidence of Timber Pest activity and/or damage resulting from Timber Pest activity is reported either in the structure(s) or the grounds of the property, then You must assume that there may be concealed structural damage within the building(s). This concealed damage may only be found when wall linings, cladding or insulation are removed to reveal previously concealed timbers. An invasive Timber Pest Inspection (for which a separate contract is required) is strongly recommended and You should arrange for a qualified person such as a Builder, Engineer, or Architect to carry out a structural inspection and to determine the full extent of the damage and the extent of repairs that may be required. You agree that neither We nor the individual conducting the Inspection is responsible or liable for the repair of any damage whether disclosed by the report or not.
5. MOULD: Mildew and non-wood decay fungi is commonly known as Mould and is not considered a Timber Pest. However, Mould and its spores may cause health problems or allergic reactions such as asthma and dermatitis in some people. No inspection for Mould was carried out at the property and no report on the presence or absence of Mould is provided. Should any evidence of Mould happen to be noticed during the inspection, it will be noted in the Other Information (5.11) section of this report. If Mould is noted as present within the property and you are concerned as to the possible health risk resulting from its presence then you should seek advice from your local Council, State or Commonwealth Government Health Department or a qualified expert such as an Industry Hygienist.
6. DISCLAIMER OF LIABILITY: No liability shall be accepted on account of failure of the Report to notify any Termite activity and/or damage present at or prior to the date of the Report in any areas(s) or section(s) of the subject property physically inaccessible for inspection, or to which access for Inspection is denied by or to the Licensed Inspector (including but not limited to any area(s) or section(s) so specified by the Report).
7. DISCLAIMER OF LIABILITY TO THIRD PARTIES: This Report is made solely for the use and benefit of the Client named on the front of this report. No liability or responsibility whatsoever, in contract or tort, is accepted to any third party who may rely on the report wholly or in part. Any third party acting or relying on this Report, in whole or in part, does so at their own risk.
8. COMPLAINTS PROCEDURE: TIn the event of any dispute or claim arising out of, or relating to the Inspection or the Report, or any alleged negligent act or omission on Our part or on the part of the individual conducting the Inspection, either party may give written Notice of the dispute or claim to the other party. If the dispute is not resolved within twenty-one (21) days from the service of the written Notice then either party may refer the dispute or claim to a mediator nominated by Us. The cost shall be met equally by both parties or as agreed as part of the mediated settlement. Should the dispute or claim not to be resolved by mediation then one or other of the parties may refer the dispute or claim to the Institute of Arbitrators and Mediators of Australia who will appoint an Arbitrator who will resolve the dispute by arbitration. The Arbitrator will also determine what costs each of the parties are to pay.
IMPORTANT MAINTENANCE ADVICE REGARDING INTEGRATED PEST MANAGEMENT FOR PROTECTING AGAINST TIMBER PESTS:
We further advise that you engage a professional pest control firm to provide a termite management program in accord with AS 3660 to minimise the risk of termite attack. There is no way of preventing termite attack. Even AS 3660 advises that “the provision of a complete termite barrier will impede and discourage termite entry into a building. It cannot prevent termite attack. Termites can still bridge or breach barriers but they can be detected more readily during routine inspections.” You should read and understand the following important information. It will help explain what is involved in a timber pest inspection, the difficulties faced by a timber pest inspector and why it is not possible to guarantee that a property is free of timber pests. It also details important information about what you can do to help protect your property from timber pests. This information forms an integral part of the report.REASONABLE ACCESS
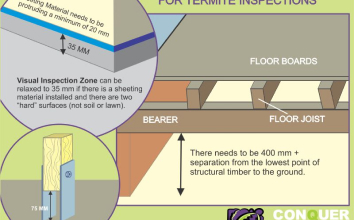
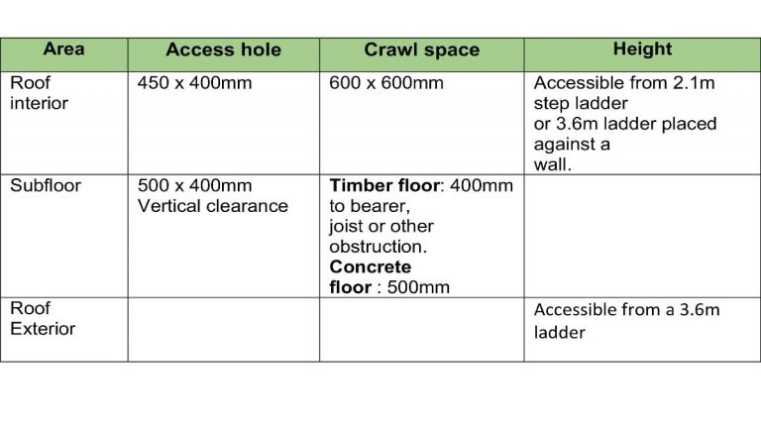
Only areas to which reasonable access is available were inspected. The Australian Standard 4349.3 defines reasonable access as “areas where safe, unobstructed access is provided and the minimum clearances specified in the Table below are available or, where these clearances are not available, areas within the consultant’s unobstructed line of sight and within arm’s length. Reasonable access does not include removing screws and bolts to access covers.” Reasonable access does not include the use of destructive or invasive inspection methods. Nor does reasonable access include cutting or making access traps, or moving heavy furniture or stored goods.
A MORE INVASIVE PHYSICAL INSPECTION IS AVAILABLE AND RECOMMENDED
As detailed above, there are many limitations to this visual inspection only. With the permission of the owner of the premises, we WILL perform a more invasive physical inspection that involves moving or lifting: insulation, stored items, furniture or foliage during the inspection. We WILL physically touch, tap, test and when necessary force/gouge suspected accessible timbers. We WILL gain access to areas, where physically possible and considered practical and necessary, by way of cutting traps and access holes. This style of report is available by ordering several days’ notice. Inspection time for this style of report will be greater than for a VISUAL INSPECTION. It involves a disruption in the case of an occupied property, and some permanent marking is likely. You must arrange for the written permission of the owner who must acknowledge all the above information and confirm that our firm will not be held liable for any damage caused to the property. A price is available on request.
CONCRETE SLAB HOMES
Homes constructed on concrete slabs pose special problems with respect to termite attack. If the edge of the slab is concealed by concrete paths, patios, pavers, garden beds, lawns, foliage, etc then it is possible for termites to affect concealed entry into the property. They can then cause extensive damage to concealed framing timbers. Even the most experienced inspector may be unable to detect their presence due to concealment by wall linings. Only when the termites attack timbers in the roof void, which may, in turn, be concealed by insulation, can their presence be detected. Where termite damage is located in the roof it should be expected that concealed framing timbers will be extensively damaged. With a concrete slab home, it is imperative that you expose the edge of the slab and ensure that foliage and garden beds do not cover the slab edge. Weep holes must be kept free of obstructions. It is strongly recommended that you have a termite inspection in accordance with AS 3660.2 carried out as recommended in this report.
SUBTERRANEAN TERMITES
No property is safe from termites! Termites are the cause of the greatest economic losses of timber in service in Australia. Independent data compiled by State Forestry shows 1 in every 5 homes is attacked by termites at some stage in its life. More recent data would indicate that this is now as high as 1 in every 3. Australia’s subterranean termite species (white ants) are the most destructive timber pests in the world. In fact, it can take “as little as 3 months for a termite colony to severely damage almost all the timber in a home”.
How Termites Attack your Home. The most destructive species live in large underground nests containing several million timbers destroying insects. The problem arises when a nest matures near your home. Your home provides natural shelter and a food source for the termites. The gallery system of a single colony may exploit food sources over as much as one hectare, with individual galleries extending up to 50 metres to enter your home, where there is a smorgasbord of timber to feast upon. Even concrete slabs do not act as a barrier; they can penetrate through cracks in the slab to gain access to your home. They even build mud tubes to gain access to above-ground timbers. In rare cases, termites may create their nest in the cavity wall of the property without making ground contact. In these cases, it may be impossible to determine their presence until extensive timber damage occurs.
Termite Damage. Once in contact with the timber, they excavate it often leaving only a thin veneer on the outside. If left undiscovered the economic species can cause many thousands of dollars damage and cost two to five thousand dollars (or more) to treat.
Subterranean Termite Ecology. These termites are social insects usually living in underground nests. Nests may be in trees or in rare instances they may be in above-ground areas within the property. They tunnel underground to enter the building and then remain hidden within the timber making it very difficult to locate them. Where timbers are concealed, as in most modern homes, it makes it even more difficult to locate their presence. Especially if gardens have been built up around the home and termite barriers are either not in place or poorly maintained. Termites form nests in all sorts of locations and they are usually not visible. There may be more than one nest on a property. The diet of termites in the natural environment is the various hardwood and softwood species growing throughout Australia. These same timbers are used in buildings. Worker termites move out from their underground nest into surrounding areas where they obtain food and return to nurture the other casts of termites within the nest.
Termites are extremely sensitive to temperature, humidity and light and hence cannot move over the ground like most insects. They travel in mud encrusted tunnels to the source of food. Detection of termites is usually by locating these mud tunnels rising from the ground into the affected structure. This takes an expert eye. Termite barriers protect a building by forcing termites to show themselves. Termites can build mud tunnels around termite barriers to reach the timber above. The presence of termite tracks or leads does not necessarily mean that termites have entered the timber though. A clear view of walls and piers and easy access to the sub-floor means that detection should be fairly easy. However many styles of construction do not lend themselves to ready detection of termites. The design of some properties is such that they make the detection by a pest inspector difficult, if not impossible.
The tapping and probing of walls and internal timbers is an adjunct or additional means of detection of termites but is not as reliable as locating tracks. The use of a moisture meter is a useful aid for determining the presence of termites concealed behind thin wall panels, but it only detects high levels of activity. Older damage that has dried out will not be recorded. It may also provide false readings. Termite tracks may be present in the ceiling space however some roofs of a low pitch and with the presence of sisalation, insulation, air conditioning ductwork, and hot water services may prevent a full inspection of the timbers in these areas. Therefore since foolproof and absolute certain detection is not possible the use of protective barriers and regular inspections is a necessary step in protecting timbers from termite attack.
BORERS OF SEASONED TIMBERS
Borers are the larvae of various species of beetles. The adult beetles lay their eggs within the timber. The eggs hatch out into larvae (grubs) which bore through the timber and can cause significant structural damage. The larvae may reside totally concealed within the timber for a period of several years before passing into a dormant pupal stage. Within the pupal case they metamorphose (change) into the adult beetle which cuts a hole in the outer surface of the timber to emerge, mate and lay further eggs to continue the cycle. It is only through the presence of these emergence holes, and the frass formed when the beetles cut the exit holes that their presence can be detected. Where floors are covered by carpets, tiling, or other floor coverings and where no access to the underfloor area is available it is not possible to determine whether borers are present or not. This is particularly the case with the upper floors of a dwelling.
Borers of ‘green’ unseasoned timber may also be present. However, these species will naturally die out as the timbers dry out in service. Whilst some emergence holes may occur in a new property it would be unusual for such a borer to cause structural damage, though the exit holes may be unsightly.
Anobium borer (furniture beetle) and Queensland pine borer. These beetles are responsible for instances of flooring collapse, often triggered by a heavy object being placed on the floor (or a person stepping on the affected area!) Pine timbers are favoured by this beetle and, while the sapwood is preferred, the heartwood is also sometimes attacked. Attack by this beetle is usually observed in timbers that have been in service for 10-20 years or more and mostly involves flooring and timber wall panelling.
The frass from the flight holes (faeces and chewed wood) is fine and gritty. Wood attacked by these borers is often honeycombed.
Lyctus borer (powder post beetle). These borers only attack the sapwood of certain susceptible species of hardwood timber. Since it is a requirement that structural timbers contain no more than 25% Lyctus susceptible sapwood these borers are not normally associated with structural damage.
Replacement of affected timbers is not recommended and treatment is not approved. Where decorative timbers are affected the emergence holes may be considered unsightly in which case timber replacement is the only option. Powder post beetles mostly attack during the first 6-12 months of service life of timber. As only the sapwood is destroyed, larger dimensional timbers (such as rafters, bearers and joists) in a house are seldom weakened significantly to cause collapse. In small dimensional timbers (such as tiling and ceiling battens) the sapwood may be extensive, and its destruction may result in collapse. Replacement of these timbers is the only option available.
TIMBER DECAY FUNGI
The fruiting bodies of wood decay fungi vary in size, shape and colour. The type of fungi encountered by pest controllers usually reside in poorly ventilated subfloors, below wet areas of the home, exterior timbers and in areas that retain water in the soil. The durability and type of timbers are factors along with the temperature and environment. Destruction of affected timbers varies with the symptoms involved. Removal of the moisture source usually alleviates the problem. Fungal decay is attractive to termites and if the problem is not rectified it may well lead to future termite attack.